Gabapentin has only three FDA indications: partial seizures, post-herpetic neuralgia, and restless legs syndrome (RLS). Gabapentin is a medication commonly used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS). RLS is a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations in the legs. Gabapentin works by affecting certain neurotransmitters in the brain, which helps to alleviate the symptoms of RLS.
It is often prescribed by doctors as a first-line treatment for RLS due to its effectiveness in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life for patients. However, like any medication, gabapentin may have potential side effects, so it’s important for individuals to discuss its use with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Although used widely in pain disorders, it only has clear benefits in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, and is not considered effective for low back pain, sciatica, spinal stenosis, or migraines (Mathieson S et al, BMJ 2020;369:m1315).
Gabapentin’s RLS approval is reserved for gabapentin enacarbil (Horizant), a prodrug that delays absorption by attaching the medication to an enacarbil molecule. However, there are three reasons to prefer the original gabapentin when treating RLS besides the higher cost of the patented Horizant:
- Convenience. Horizant must be taken with a meal at 5:00 p.m. Gabapentin can be taken before bed regardless of food.
- Driving. The PDR warns of “significant driving impairment” for two hours after taking Horizant, a problem that is compounded by alcohol, which quickens Horizant’s release. This is an issue for patients who dine out, while gabapentin can be taken right before bed without affecting driving the next morning.
- Toxicity. The enacarbil in Horizant breaks down into acetaldehyde, the same byproduct responsible for the carcinogenic and hangover effects of alcohol. The FDA originally rejected the drug over this issue, and Horizant still carries a warning about “chromosomal aberrations” in human lymphocytes “attributed to acetaldehyde.”
Although lacking in FDA approval, the original gabapentin was effective for RLS in half a dozen small studies. The usual dose is 300 mg before bed (which is equivalent to 600 mg of Horizant), but studies have gone as high as 2400 mg.
What is Restless Legs Syndrome ?
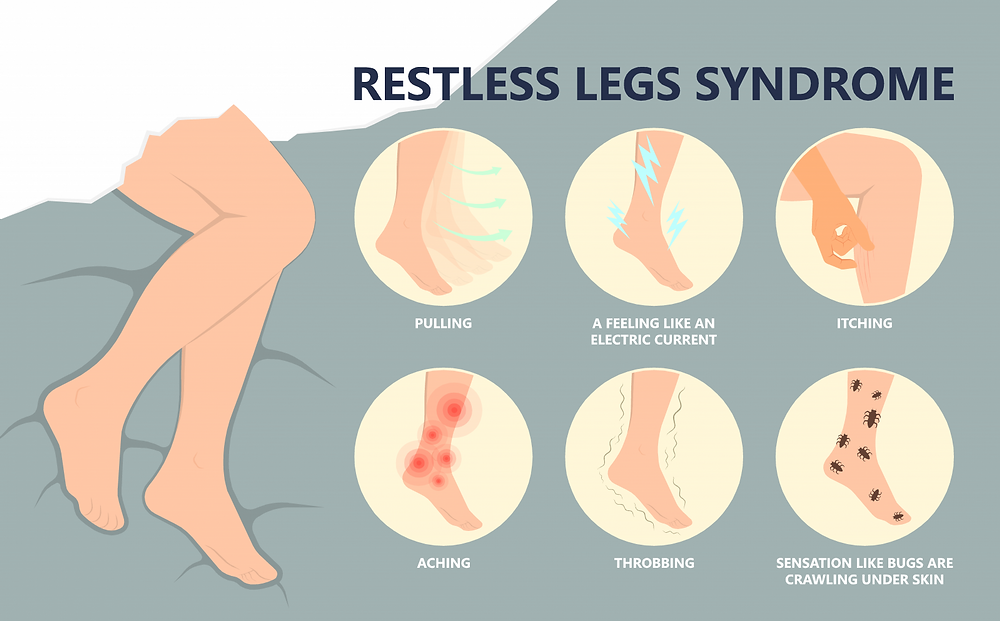
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS), also known as Willis-Ekbom disease, is a neurological disorder characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs. People with RLS often experience uncomfortable sensations in their legs, such as tingling, itching, crawling, or aching sensations, particularly when at rest or during periods of inactivity. These sensations can be relieved temporarily by moving the legs, stretching, or walking.
RLS symptoms typically worsen in the evening or at night, which can disrupt sleep and lead to insomnia. The exact cause of RLS is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve abnormalities in the brain’s dopamine system and disruptions in iron metabolism.
RLS can range from mild to severe and may be intermittent or chronic. It can significantly impact quality of life, causing discomfort, sleep disturbances, and daytime fatigue. Treatment for RLS may include lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and using medications like dopamine agonists, anticonvulsants (such as gabapentin), or opioids to alleviate symptoms and improve sleep. Individuals experiencing symptoms of RLS should consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
